SLIPPERY ELM
red elm
Ulmus rubra Muhlenberg
|
| Slippery elm is a medium-sized forest tree of stream banks and low fertile slopes and is common south of the Adirondacks. The wood is hard, heavy, strong, coarse-grained, and fairly durable in contact with the soil. This tree is not an important commercial species but is used for fence posts, ties, barrel staves and hoops. |
| Bark - grayish brown in color, more or less deeply furrowed, the ridges tending to lift more along one edge than in the American elm; layers of outer bark reddish brown in color, shows no alternate layers of brown and white as in the American elm; inner bark, next to the wood, whitish, strongly mucilaginous (like glue), giving the name "slippery elm."
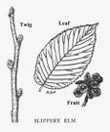
Twigs - light gray in color, hairy, somewhat rough, characteristically mucilaginous when chewed.
Winter buds - terminal bud absent as in American elm; lateral buds 1/4 inch long, dark chestnut brown in color, covered at tip with long, rusty hairs.
Leaves - alternate, simple, oval, 5 to 7 inches long, oblique at the base, margin doubly serrate; at maturity thick, dark green in color above, decidedly rough to the touch, paler and white-hairy below; midrib and parallel veins prominent.
Fruit - flat-winged, but not notched at the end, 1/2 to 3/4 inch long, containing one seed; in clusters, maturing in late May or early June when the leaves are about half grown, falling soon thereafter.
Distinguishing features - inner bark chewy, without alternate layers of brown and white; leaf base oblique, rough above and below; twigs chewy; buds tipped with rusty hairs.
|
No comments:
Post a Comment